Automated Shaft Cutting Machine
Fall 23 - Senior Design Capstone
Project Description Summary
REEKON is a company that designs innovative hardware tools and software to streamline communication across projects on the jobsite. Their team frequently uses steel rods of various sizes for manufacturing purposes. Steel rods come in stock sizes that need to be cut to varying lengths depending on the application. Cutting steel rods typically involves manually using hacksaws or a dremel cutting tool with abrasive discs made of hard ceramic and reinforced with fiberglass.
This process can be extremely time consuming and tedious, and often results in inaccurate cuts. Our client's goal for the senior design project was to have us automate this process in order to increase accuracy, time efficiency, and ease of use.
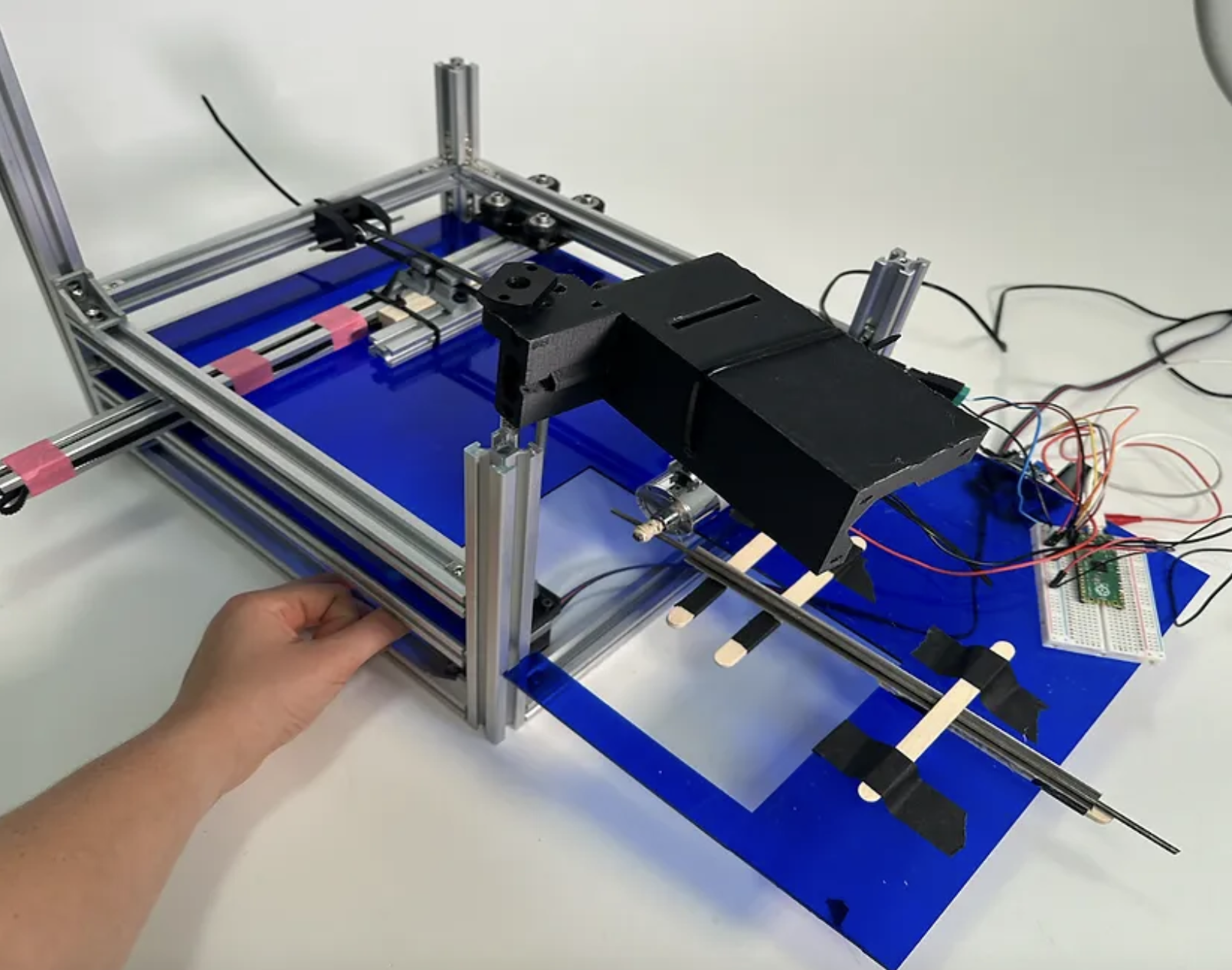
Through many stages of prototypes and reviewing with both the client and experts, we decided to divide the process into the following main steps: receive user input, measure out the cut, feed in the rod, lower the cutting device, and retrieve the newly cut rod.
In order to receive user input, we used the Airtable Application Programming Interface to provide users with a survey-like format asking about the diameter of the rod and the cut they wish to be made. After, the user places the rod into the v-slot. The alternating pattern of 45 degree angled rectangles acts as a clamp for the rod during the cutting process, as a force is applied at alternating directions. Inspired by 3D printers, we created a belt driven stepper motor system that drives an 8020 bar a specified distance that the rod gets fed in to. The distance between the 8020 bar and the cutting disc is the length of rod that will be cut. Next, a DC motor with rubber bands attached activates and feeds in the rod. Rubber bands were used so that when wear down occurs, manufacturers can replace the rubber bands, as they are a common office supply. The rod hits the block then stops, thus at the distance for the correct cut to be made. Modeling after how rods are cut manually, we used a dremel for the actual cutting of the rod. Once the rod is in the proper position, the dremel lowers on two lead screws. After the cut is complete, the rod rolls down a ramp and into a metal catch tray for retrieval of the user.
The process is now fully automated and only requires the user to place the rod and input their information. The product enables users to have accurately cut, custom length rods for any manufacturing purposes.
Design Breakdown
Parts of the Machine:
Cutting
Measuring
Feed-In/Feed-Out
User Interface
Cutting:
Cutting Device: Dremel with 3” Cut Off Wheel
Motion: Linear
Two stepper motor linear actuators
Cutting Speed:
determined by both the steps of the motor and the speed of the wheel
motor steps: 20 seconds per 10 steps
speed of the Dremel: 6 - 20,000 rpm
Measuring:
Components:
Blocker (8020) on a belt
Stepper Motor
How it works:
Blocker gets moved to the appropriate position base don user input
Rod gests fed in by dc motor until it hits the blocker
Feed In/Feed Out:
Feed-In:
Motor with spindle of rubber bands spins the rod in using friction
Feed-Out:
Once the rod is cut it will roll down the ramp into a catch tray
User Interface
Airtable API
User inputted data connected directly with running processes